How to Become a Licensed US Pharmacist: A Step-by-Step Guide

The profession of pharmacy is one of the most rewarding and dynamic healthcare careers in the United States.
Although, its challenging but its a highly rewarding journey, i can tell you that much.
Just so you know!.. Pharmacists are healthcare professionals responsible for the safe distribution of medications, patient education, and drug therapy management.
With their in-depth knowledge of pharmaceuticals, pharmacists play an essential role in ensuring that individuals receive the proper treatment for their conditions and are educated on how to use medications safely.
If you have a passion for science, health, and helping others, becoming a pharmacist in the USA could be the ideal career for you. However, the journey to becoming a licensed pharmacist in U.S requires dedication, education, training, and a commitment to lifelong learning.
Therefore, in this comprehensive step-by-step guide, we will explore with details, paths and steps you need to take to become a licensed pharmacist in the United States (USA), from high school down to your professional practice.
Role of a Licensed Pharmacist
Before you embark on the road to becoming a pharmacist, it’s important to understand the key responsibilities of the profession and ask yourself the question, Why! Pharmacy and if a career in Pharmacy is worth it?.
Again, Pharmacists are healthcare professionals who:
- Dispense Medications: Ensure patients receive the correct medication and proper dosage.
- Provide Medication Counseling: Advise patients on how to take their medications safely, potential side effects, and drug interactions.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Help patients manage long-term conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma through medication therapy management.
- Collaborate with Healthcare Teams: Work closely with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare providers to optimize patient care.
- Monitor Medication Therapy: Keep track of a patient's medication regimen to prevent adverse drug reactions and improve therapeutic outcomes.
Pharmacists 👩⚕️ typically work in a variety of settings, including retail pharmacies, hospitals, outpatient clinics, pharmaceutical companies, and academic institutions.
Their role is indispensable in providing safe and effective medication therapies to patients.
Steps to Become A Licensed US Pharmacist
1. Obtain a High School (Secondary school ) Diploma / cert.
Your journey to becoming a pharmacist begins as early as high school (or secondary school, for feign students / aspirate - for example: some counties after secondary school next is university).
While there’s no official pre-pharmacy high school program, taking certain courses can help you lay a solid foundation for your future studies in pharmacy school.
Focus on courses like: 📚
- Mathematics: Algebra, calculus, and statistics are crucial for understanding drug dosages and calculations.
- Science: Chemistry, biology, and physics provide the fundamental scientific knowledge required for pharmacy coursework.
- English and Communication: Strong communication skills are essential when advising patients and collaborating with healthcare professionals.
- Health and Anatomy: Basic knowledge of the human body and its functions is useful when learning pharmacology and therapeutics.
- Additionally, gaining experience in a healthcare setting—such as volunteering at a hospital, shadowing a pharmacist, or working in a pharmacy—can be incredibly valuable.
Not only does it give you a glimpse into the day-to-day life of a pharmacist, but it also allows you to build experience and connections within the healthcare industry.
2. Complete a Pre-Pharmacy Program (Optional)
In the United States, some pharmacy schools accept students directly from high school into a six-year program that combines undergraduate and doctoral-level education.
However, most students opt to complete a pre-pharmacy program or earn a Bachelor’s degree before applying to pharmacy school.
Pre-pharmacy programs or educations are designed to prepare students for pharmacy school by providing foundational coursework in subjects such as:
- General Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Biology
- Mathematics
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Microbiology
- Pharmacology
These courses will build the scientific knowledge you need to succeed in pharmacy school and the pharmacy profession.
Some students may choose to major in a related field such as biology, chemistry, or health sciences during their undergraduate studies, while others may select a general pre-pharmacy program.
The completion of a pre-pharmacy program typically takes two to four years, depending on whether you attend a community college or a four-year university.
And as for Foreign students, who wish to become a licensed pharmacist in U.S., especially those from Africa, a recognizable certificate (example:- West African Examinations Council (WAEC)) form your home county would take you to the next step below.
3. Apply to a Pharmacy School ( University )
Pharmacy schools are competitive, so your academic performance during your undergraduate years will be important.
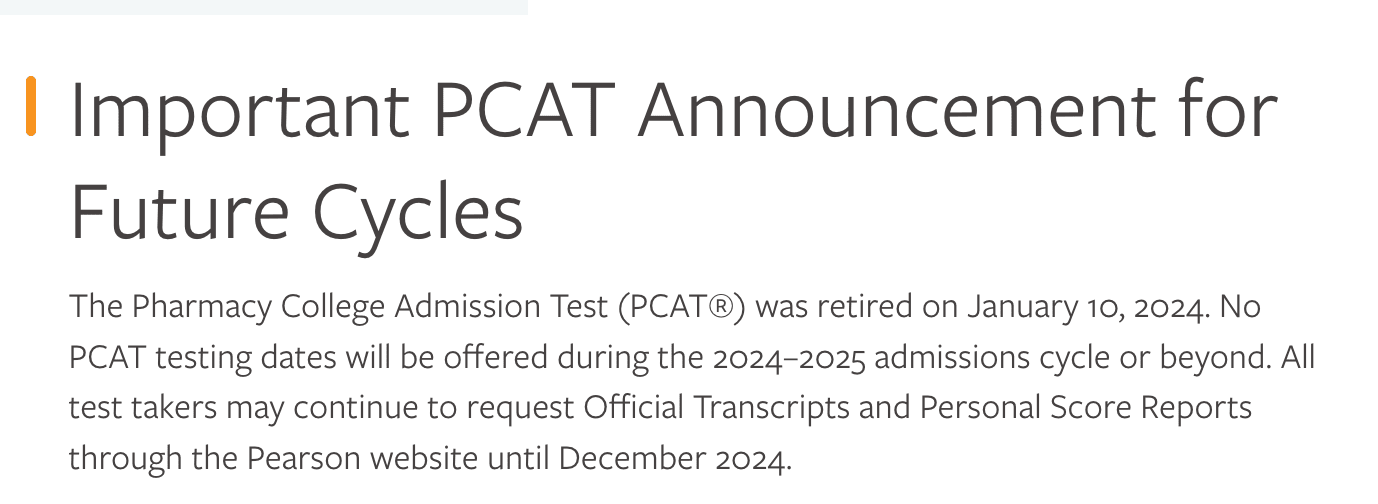
Most students (foreign students mostly) take the Pharmacy College Admission Test (PCAT), a standardized exam that assesses your knowledge of scientific concepts, reading comprehension, and quantitative reasoning.
However, some schools may not require the PCAT, so check individual school requirements. But, seems the PCAT has been officially STOPPED
Hence, to become a licensed pharmacist, you must earn a Pharm.D. degree from an accredited pharmacy school.
The program typically takes four years to complete and includes coursework in:
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacy law and ethics
- Patient care
- Medication therapy management
Many programs also include hands-on clinical rotations in various healthcare settings to provide practical experience.
You can search for accredited pharmacy schools on the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE) website.
4. Complete Internships and Clinical Rotations
During pharmacy school (University), you’ll be required to complete a set number of clinical rotations and internships hours.
These hands-on experiences allow you to apply the knowledge you’ve gained in real-world settings and work under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist to provide patient care.
This clinical training is an essential part of your education and will prepare you for the responsibilities you’ll face as a licensed pharmacist.
NOTE: This also applies to foreign pharmacist, who wish to relocate to the US.
5. Pass the Licensure Exams
To legally practice as a pharmacist in the United States, you must pass several licensure exams.
The two main exams are:
- North American Pharmacist Licensure Examination (NAPLEX): The NAPLEX tests your knowledge of pharmacy practice, including drug therapy, medication management, and patient care.
Passing this exam is a requirement for licensure in all 50 states.
- Multistate Pharmacy Jurisprudence Examination (MPJE):
The MPJE tests your knowledge of pharmacy law, including state and federal regulations that govern pharmacy practice.
Each state has its own laws, so it’s important to study accordingly.
Tips: Use the RxQuix app, as a study guide. Also check with your state’s Board of Pharmacy for specific additional details.
You can find more information about licensure on the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP) website.
6. Apply for State Licensure
After passing the NAPLEX and MPJE, you can apply for a pharmacist license in your state.
Requirements vary by state, so You can contact your state’s Board of Pharmacy to begin the licensure application process and ensure you meet all the state-specific requirements.
7. Consider Specializations and Certifications (Optional)
CONGRATULATIONS ! ! Now you’ve obtained your pharmacist license, you may wish to specialize in a specific area of pharmacy practice.
Some pharmacists choose to pursue certifications in areas such as:
- Board Certification in Pharmacotherapy (BCPS)
- Board Certification in Oncology Pharmacy (BCOP)
- Board Certification in Ambulatory Care Pharmacy (BCACP)
These certifications can help you specialize in areas such as hospital pharmacy, oncology, pediatrics, or psychiatric pharmacy.
Specializations can open up more career opportunities and increase earning potential.
🤔 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) ⁉️
❓: How long does it take to become a pharmacist in the US?
✅ : It typically takes 6-8 years to become a pharmacist, including undergraduate coursework, a Pharm.D. program, and licensure.
❓: Can international students become pharmacists in the US?
✅ : Yes, international students can become pharmacists in the US, but they must meet the same educational and licensing requirements as US citizens.
Additional steps may include obtaining a visa and passing English proficiency exams.
❓: What is the difference between a pharmacist and a pharmacy technician?
✅ : Pharmacists hold a Pharm.D. degree and are licensed to dispense medications and provide patient care.
Pharmacy technicians assist pharmacists with tasks like filling prescriptions and managing inventory but do not require a doctoral degree.
see article :- Pharmacist vs. Pharmacy Technician: Understanding the Key Differences
❓: How long does it take to study for NAPLEX ?
✅ : Its best that you start studying at least six months before your test. Use the RxQuiz App or NAPLEX online video lectures to help you study.
❓: What is the passing score for the NAPLEX?
✅ : 75 or greater - The overall NAPLEX scaled scores range from 0 to 150.
Good luck ..... Please like and share.